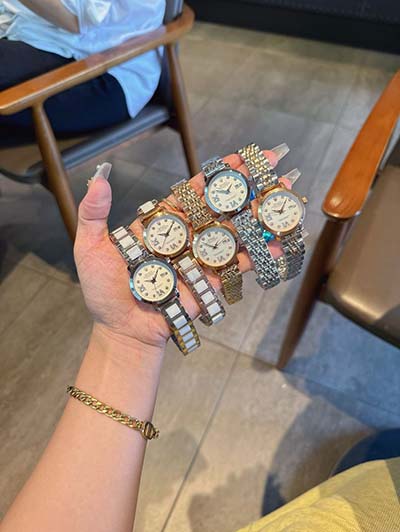
hearbest mi robot hermes Oct 30, 2019 — The main components of MIT’s bipedal robot Little HERMES: (A) Custom actuators designed to withstand impact and capable of producing high torque. (B) Lightweight limbs with low inertia and fast .
NEWS. EDC Las Vegas 2020 is still on. But organizers are prepared to postpone as COVID-19 spreads. Ed Komenda. Reno Gazette Journal. 0:00. 0:55. LAS VEGAS – The sold-out Electric Daisy.
0 · mit's hermes robot
1 · mit hermes robot footing
2 · mit hermes rescue
3 · mit hermes human reflexes
4 · little hermes robot
5 · hermes robot
6 · hermes bipedal robot
EDC Production Crew Producer: Insomniac ProductionsExecutive Producer: Forrest HuntProduction Director: Alyxzander BearProduction Designer/LD: Stephen Lieberman/SJ Lighting
hearbest mi robot hermes*******Aug 10, 2015 — HERMES, a bipedal robot (foreground) designed for disaster response, punches through drywall while keeping its balance, guided by a human operator (background).hearbest mi robot hermes mit hermes rescueDeep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash .
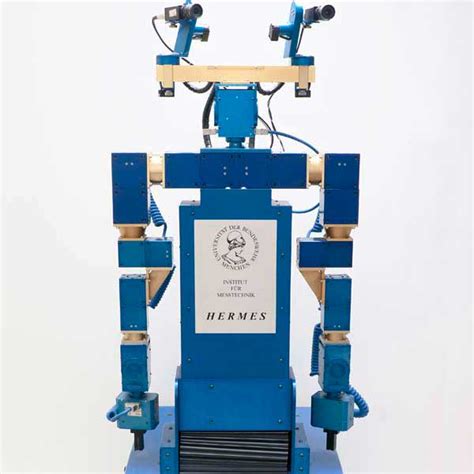

Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash .
May 28, 2019 — MIT’s Hermes is a bipedal robot that uses full-body teleoperation to move with greater agility. Photo: Bob O’Connor. Dynamic Duo: MIT’s João Ramos wears a .Mechanical engineers from MIT have designed an interface that takes advantage of a human's split-second reflexes, allowing a humanoid to maintain its balance and .hearbest mi robot hermesOct 30, 2019 — The main components of MIT’s bipedal robot Little HERMES: (A) Custom actuators designed to withstand impact and capable of producing high torque. (B) Lightweight limbs with low inertia and fast .mit hermes rescueOct 30, 2019 — The main components of MIT’s bipedal robot Little HERMES: (A) Custom actuators designed to withstand impact and capable of producing high torque. (B) Lightweight limbs with low inertia and fast .
Dynamic Duo: MIT’s João Ramos wears a teleoperation suit that connects his body to that of HERMES, a bipedal robot designed for disaster response. Ramos’s reflexes help HERMES keep its footing.
HERMES, a bipedal robot (foreground) designed for disaster response, punches through drywall while keeping its balance, guided by a human operator (background).Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half.

Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half.
MIT’s Hermes is a bipedal robot that uses full-body teleoperation to move with greater agility. Photo: Bob O’Connor. Dynamic Duo: MIT’s João Ramos wears a teleoperation suit that connects his body to that of HERMES, a bipedal robot designed for disaster response.Mechanical engineers from MIT have designed an interface that takes advantage of a human's split-second reflexes, allowing a humanoid to maintain its balance and complete tasks. A two-legged robot named HERMES, outfitted with load sensors, can punch through drywall, smash soda cans, and karate-chop boards in half, but its actions are not its own. The main components of MIT’s bipedal robot Little HERMES: (A) Custom actuators designed to withstand impact and capable of producing high torque. (B) Lightweight limbs with low inertia and fast leg swing. (C) Impact-robust and lightweight foot sensors with three-axis contact force sensor.Engineers have developed a new method to control balance for the bipedal HERMES robots using a vest that relays human motion to direct the robots. (📷: MIT) The robots are controlled remotely by human operators who wear a specially designed vest that transmits the person’s motion and ground reaction forces over to HERMES. HERMES is a humanoid robot that can perform human movements, with MIT researchers using what is known as balance-feedback interface to control the robot.
Called Little Highly Efficient Robotic Mechanisms and Electromechanical System (HERMES), the small-scale bipedal robot is a third of the size of an adult person and can run, jump, and mostly. Dynamic Duo: MIT’s João Ramos wears a teleoperation suit that connects his body to that of HERMES, a bipedal robot designed for disaster response. Ramos’s reflexes help HERMES keep its footing.
HERMES, a bipedal robot (foreground) designed for disaster response, punches through drywall while keeping its balance, guided by a human operator (background).Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half.Deep in the basement of MIT’s Building 3, a two-legged robot named HERMES is wreaking controlled havoc: punching through drywall, smashing soda cans, kicking over trash buckets, and karate-chopping boards in half.
MIT’s Hermes is a bipedal robot that uses full-body teleoperation to move with greater agility. Photo: Bob O’Connor. Dynamic Duo: MIT’s João Ramos wears a teleoperation suit that connects his body to that of HERMES, a bipedal robot designed for disaster response.Mechanical engineers from MIT have designed an interface that takes advantage of a human's split-second reflexes, allowing a humanoid to maintain its balance and complete tasks. A two-legged robot named HERMES, outfitted with load sensors, can punch through drywall, smash soda cans, and karate-chop boards in half, but its actions are not its own. The main components of MIT’s bipedal robot Little HERMES: (A) Custom actuators designed to withstand impact and capable of producing high torque. (B) Lightweight limbs with low inertia and fast leg swing. (C) Impact-robust and lightweight foot sensors with three-axis contact force sensor.
Engineers have developed a new method to control balance for the bipedal HERMES robots using a vest that relays human motion to direct the robots. (📷: MIT) The robots are controlled remotely by human operators who wear a specially designed vest that transmits the person’s motion and ground reaction forces over to HERMES.
Atlaides. Veikali. Premium. Jaunums -50% 90 € 180 € ECCO. Premium. -29% 119,99 € 170 € ECCO. Premium. -8% 109,99 € 120 € ECCO. Premium. -50% 85 € 170 € ECCO. Premium. -50% 95 € 190 € ECCO. Premium. -50% 90 € 180 € ECCO. Premium. Jaunums -50% 85 € 170 € ECCO. Premium. Jaunums -50%
hearbest mi robot hermes|mit hermes rescue